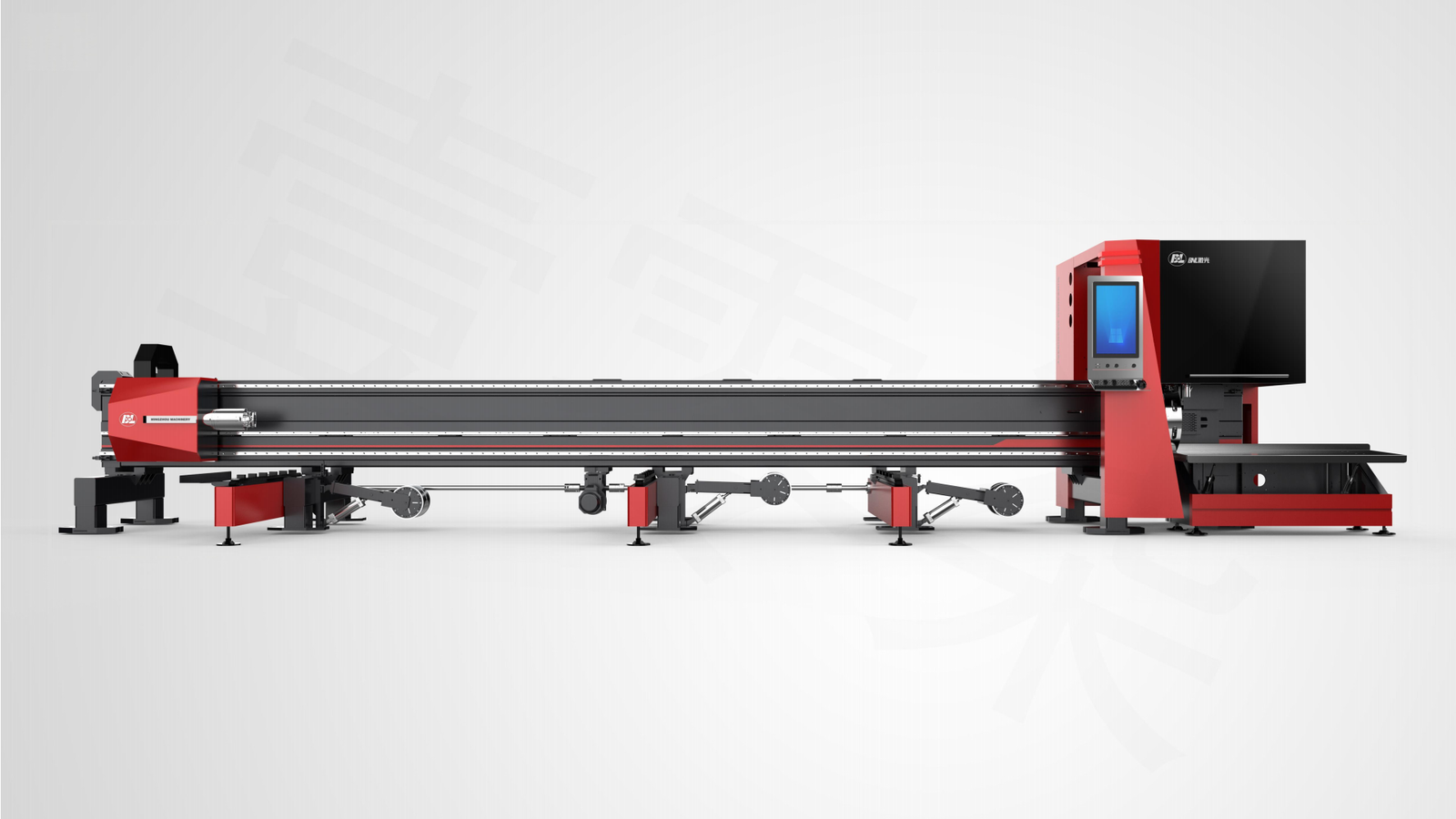
The 4 Main Types of Laser Cutting Machines (and Their Applications)
Choosing the right laser cutter is complex. A wrong choice costs money and time. Understanding the four main types simplifies your decision and boosts your factory's a efficiency.
The four main types of laser cutting machines are CO2, fiber, Nd:YAG, and diode. CO2 lasers excel with non-metals like wood and acrylic. Fiber lasers are best for cutting metals with high speed and efficiency. Nd:YAG is used for high-power welding, and diode lasers offer energy-efficient fine processing.

I've been in this industry for over a decade, and I've seen how the right technology can completely transform a production line. The key is not just buying a machine, but buying the right machine for your specific job. Let's break down how laser technology has evolved and what your options are today.
How Has Laser Cutting Technology Evolved?
Early laser machines were complex and slow. They required highly skilled operators. Now, modern machines are faster, smarter, and much easier for anyone on your team to use.
Laser cutting has evolved from slow, specialized tools into highly efficient, automated systems. Key advancements include increased power, speed, and user-friendly interfaces, making the technology more accessible and versatile for modern manufacturing needs. This evolution has drastically reduced the need for extensive operator training.
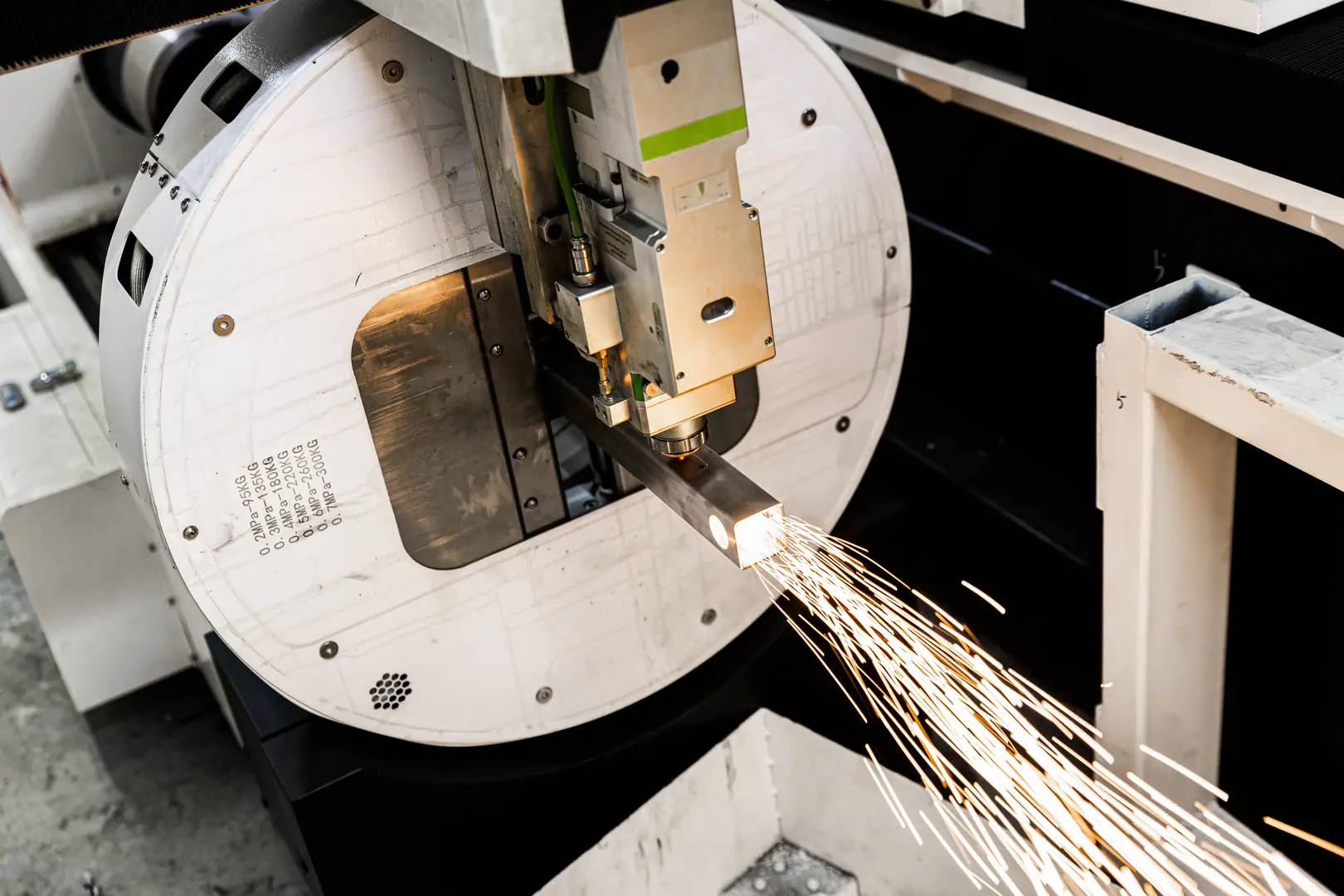

I remember visiting a factory about fifteen years ago. They had a massive CO2 laser cutter that took up a huge amount of floor space. It required a dedicated engineer with weeks of training just to operate it. The process was slow, and setup was complicated. Fast forward to today, and the difference is incredible. When I walk through our clients' facilities, I see our compact fiber laser tube cutters running at speeds that were once unimaginable. More importantly, the operator who started just that morning is already producing perfect parts. This is the real evolution: we've moved from complex tools for specialists to accessible, powerful machines for any modern manufacturer. This change was driven by the need for greater efficiency, lower labor costs, and the ability to adapt quickly to new customer demands. The technology has become a true partner in production, not a bottleneck.
What Types of Laser Cutting Machines Are Available Today?
You see many machine types on the market. It is confusing to know the difference. Here is a clear breakdown to help you understand your options.
The four main types are CO2, fiber, Nd:YAG, and diode lasers. CO2 is best for organic materials, fiber excels with metals, Nd:YAG is for welding and drilling, and diode lasers are energy-efficient for fine processing and engraving.

Choosing the right laser source is the most critical decision you will make. It directly impacts your productivity, operational costs, and the quality of your finished products. At MZBNL, we focus primarily on fiber laser technology because it offers the best performance for the metal tube processing industry, but understanding all four types is essential.
The Four Core Technologies
Here’s a simple table to compare the main types:
| Laser Type | Primary Use Cases | Key Advantages | Key Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Laser | Metal cutting (steel, aluminum, brass), marking | High speed, high efficiency, low maintenance, long lifespan | Higher initial cost, not suitable for non-metals |
| CO2 Laser | Cutting non-metals (wood, acrylic, plastic, paper), engraving | Excellent cut quality on organic materials, versatile | Slower on metals, higher maintenance (gas, mirrors) |
| Nd:YAG Laser | Welding, drilling, marking on metals and plastics | High peak power, can cut thick materials | Lower efficiency, shorter lifespan of consumables |
| Diode Laser | Engraving, plastic welding, fine material processing | Very energy efficient, compact size, long lifespan | Lower power, limited cutting applications |
For most of our clients in furniture, automotive parts, or sanitary ware manufacturing, the choice is clear. They need the speed and precision of a fiber laser to stay competitive.
What Are the Challenges in Selecting a Laser Cutting Machine?
Buying a new machine is a big investment. A mistake is very costly. We can help you avoid the common pitfalls that hurt your ROI.
The main challenges are matching the laser type to your specific materials, balancing the initial purchase price against long-term operational costs, and overcoming the operator skill gap. Choosing incorrectly leads to poor performance, high waste, and wasted investment.

One of the biggest hidden challenges I see clients face is the total cost of ownership[^1]. A machine might have an attractive price tag, but if it consumes a lot of power, requires expensive maintenance, or needs a highly paid specialist to run, it's not a good investment. Another major issue is the growing skills gap. It is getting harder to find and retain operators with years of technical experience. This is a problem we took very seriously at MZBNL. We believe that powerful technology should be simple to use. Your machine should not be dependent on one single expert. It should be a tool that any trained member of your team can operate safely and efficiently. That's why we invested heavily in creating intuitive control systems that turn a multi-week training process into a single day. This directly addresses the skills gap and gives our clients more flexibility in their operations.
How Do You Choose the Right Laser Cutting Machine for Your Application?
You need a clear plan to choose a machine. Guessing is not a strategy. Follow these simple steps to make a smart, data-driven decision for your business.
To choose the right machine, first analyze your primary materials and required cutting thickness. Then, evaluate your production volume needs to determine the required speed and automation. Finally, calculate the total cost of ownership, not just the purchase price.

Making the right choice comes down to a methodical process. Over the years, I've helped hundreds of business owners walk through these steps to ensure they get the perfect fit for their factory.
Step 1: Analyze Your Materials and Thickness
What are you cutting 80% of the time? Is it 2mm stainless steel tube or 20mm acrylic sheet? Be specific. A fiber laser is the champion for metal tubes, while a CO2 laser is necessary for the acrylic. This single question will narrow your options dramatically.
Step 2: Define Your Production Needs
Are you running small, custom batches or high-volume, continuous production? Your answer determines the level of automation you need. For high-volume work, features like automatic loading and unloading are not luxuries; they are essential for profitability. Speed is also critical here. A faster machine can produce more parts per hour, directly impacting your bottom line.
Step 3: Consider the Operator
Who will be running this machine? Do you have experienced engineers on staff, or do you need a machine that new employees can learn quickly? This is where software and user interface become critical. For example, our MZBNL machines include a No-CAD System. This allows an operator to select a pre-programmed cutting pattern directly on the machine's interface without needing a separate engineer to create a CAD file. This innovation alone saves our clients hours of downtime and makes their production far more agile.
How Can You Optimize Your Laser Cutting Machine's Performance?
You bought the machine. Now you must get the most from it. Poor optimization wastes valuable material, energy, and time, directly eating into your profits.
Optimize performance by using the correct assist gas, maintaining clean optics, and programming efficient cutting paths. Regular preventative maintenance and leveraging advanced software features are also critical for maximizing output and material usage.
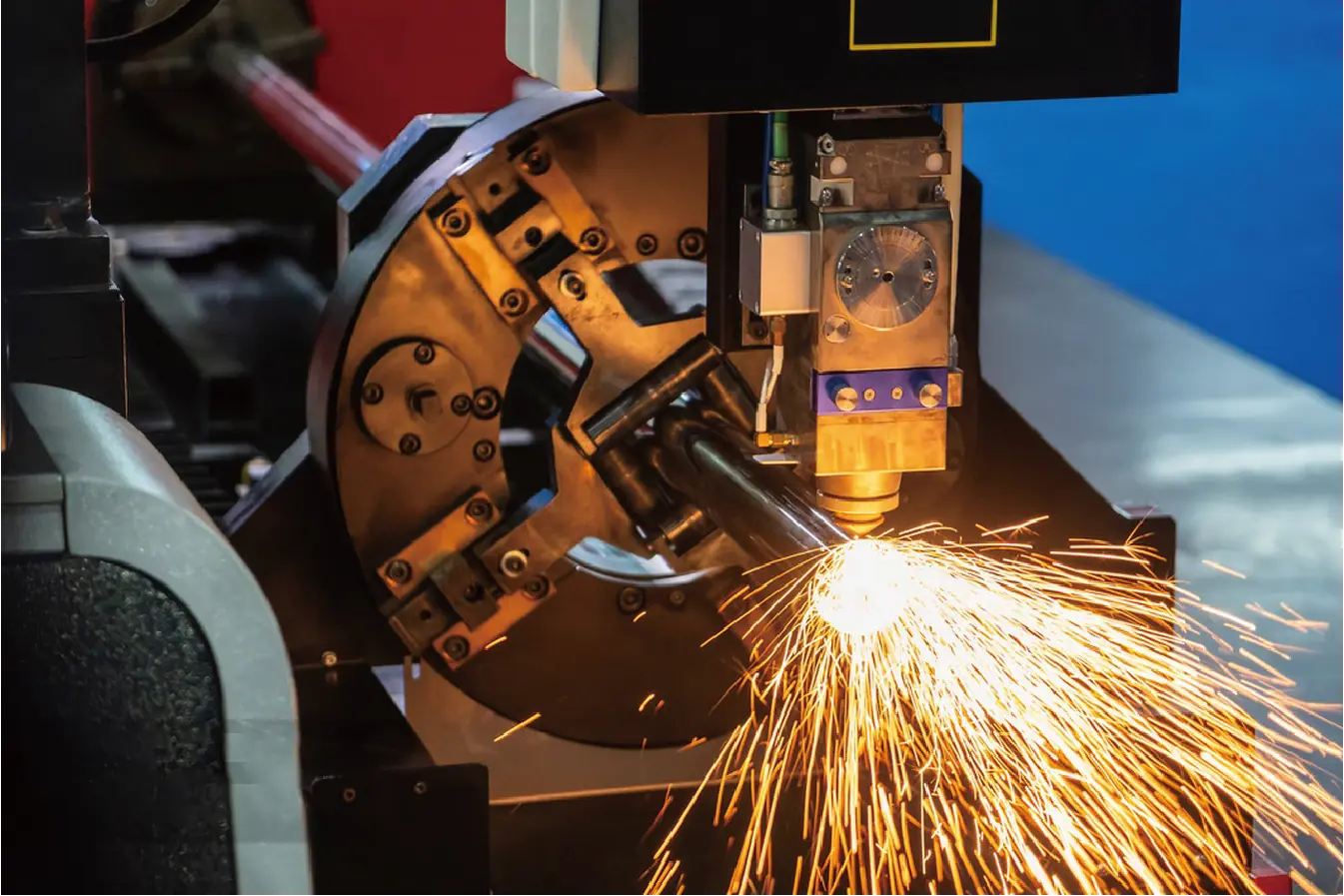

I recently visited a client who was producing metal furniture. They had a good machine, but their material waste was high. At the end of every 6-meter metal tube, they were left with a 300mm piece of tail material that was thrown away as scrap. Over a year, this added up to thousands of dollars in waste. This is a common problem, and it's one we solved with our Zero-Waste Tail Material Innovation[^2]. By redesigning the machine's chuck system, we reduced that unusable tail material from 300mm down to just 40mm. This single feature provided an immediate and measurable ROI for our client. Optimization isn't just about speed; it's about intelligence. It's about looking at every part of the process—from software to hardware—to eliminate waste and maximize the value you get from your raw materials and your machine investment.
Conclusion
Understanding the four main laser types is the first step. The next is matching the right technology to your materials, production goals, and your team. By focusing on total cost, ease of use, and material efficiency, you can make a smart investment that pays for itself.
Have Questions or Need More Information?
Get in touch with us for personalized assistance and expert advice.